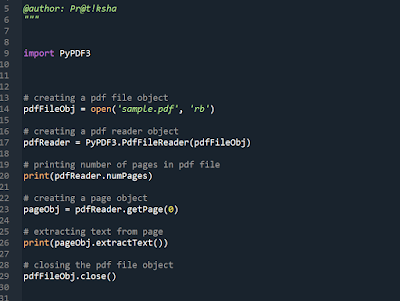
Pillow Libary in Python.
Pillow library: It is a lightweight image processing tool that aid in editing, creating, and saving images. Pillow supports many image file formats including BMP, PNG, JPEG, and TIFF. Python Imaging Library is a free and open-source additional library for the Python programming language that adds support for opening, manipulating, and saving many different images file formats.
How to install pillow: pip install Pillow
The
most important class in the Python Imaging Library is the Image class. Defined in the module
with the same name. You can create instances of this class in several ways.
Open(): You
can use an open () function in the Image module.
from PIL import
Image
img = Image.open(“car.jpg")
The
PIL.Image.Image class represents the image object. This function returns
an Image object. You can now use instance attributes to examine the file
contents.
print (img.format,
img.size, img.mode)
Format:
The format attribute identifies the source of an image. If the image was not
read from a file, it is set to None.
Size:
This attribute provides the
size of the image. The size attribute is a 2-tuple containing width and height
(in pixels).
Mode:
attribute defines the number and names of the bands in the image, and the pixel
type and depth. Common modes are “L” (luminance) for greyscale images, “RGB”
for true color images, and “CMYK” for pre-press images.
Getting the mode
of the image:
The
mode attribute of the image tells the type and depth of the pixel in the image.
1. 1: 1-bit pixel has a range of 0-1, black and white.
2.
L: 8-bit pixel has a range of 0-255, Greyscale.
3.
P: 8-bit pixels, mapped to any other mode using a color
palette.
4.
RGB: 3X8 bit pixels, true-color with transparency mask.
How
to display an image?
img.show()
This
method is used to display the image. For displaying the image Pillow first converts the image to
a .png format (on Windows OS) and stores it in a temporary buffer and then
displays it.
Save():
To save a file, use the save () method of the Image class. While using the save()
method Destination_path must have the image filename and extension as well. The
extension could be omitted in Destination_path if the extension is specified in
the format argument.
The
Image class contains methods allowing you to manipulate regions within an
image. To extract a sub-rectangle from an image, use the crop () method.
Resizing an image using resize(): Interpolation happens during the resize process, due to which the quality of the image changes whether it is being upscaled (resized to a higher dimension than original) or downscaled (resized to a lower Image than original).
Filters:
- PIL.Image.NEAREST: Pick one nearest pixel from the input image. Ignore all other input pixels.
PIL.Image.BOX: Each pixel of the source image contributes to one pixel of the destination image with identical weights. This filter can only be used with the resize () and thumbnail () methods.
The output of cropping:
The output of the show method:







Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubt, please let me know. To check my other blog kindly check the following links:
https://pythoholic.blogspot.com/
If you are interested in reading Marathi stories and other stuff, kindly check the following link.
https://pratilipi.page.link/q8dZ4ffZwKPHUx6R9
ꜰᴏʀ ᴇxᴘʟᴏʀɪɴɢ ᴛʜᴇ ᴡᴏʀʟᴅ ᴘʟᴇᴀꜱᴇ ʜᴀᴠᴇ ʟᴏᴏᴋ ᴀɴᴅ ꜰᴏʟʟᴏᴡ.
https://maps.app.goo.gl/jnKyzdDpKMFutUqR7